Astaxanthin is a type of carotenoid with a reddish pigment that can be found in some types of algae, fungi, mollusks or salmon.
In recent years, astaxanthin popularity has risen since it has shown in various studies its multiple benefits in different health areas when it is consumed as a supplement.
What is astaxanthin and where to find it
As it has been mentioned before, astaxanthin is a carotenoid from the group of xanthophylls (a type of pigment that is found naturally in plants, as is the case of lutein that gives a greenish-yellow color to lettuce) that has shown to have one of the highest antioxidant powers.
As an antioxidant, astaxanthin has been shown to have multiple properties that improve vision, skin condition, fertility, cardiovascular health…
Astaxanthin is mainly found in a type of algae called haematococcus pluvialis or in a type of yeast called xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous, although because many species feed with these algae we can also find it in salmon, in some types of crayfish, and in some crustaceans like krill among others.
Currently, it is mainly consumed in natural supplements whose source of astaxanthin is usually the algae H. pluvialis, which makes it more bioavailable and better absorbed than artificial astaxanthin, so you should always make sure that your supplement comes from a natural source.
Generally it is almost impossible to achieve astaxanthin benefits by consuming salmon and the other foods mentioned above since they do not contain a considerable amount to achieve its health properties, so if you want to benefit you must take it as a supplement.
What makes astaxanthin special alongside other antioxidants
In addition to having a far superior antioxidant power compared to other antioxidants, astaxanthin never oxidizes and never becomes a pro-oxidant.
Antioxidants neutralize the effects of free radicals in the body, these free radicals in large amounts can accelerate aging and worsen health, however some antioxidants have shown that when they are consumed from a certain high amount or when they are exposed to external stress become pro-oxidants, which instead of benefitting us, worsen our health. This never occurs with astaxanthin.
Astaxanthin has been shown (as an antioxidant level) to be up to 6,000 times more potent than vitamin C, 3,000 times more than resveratrol, 800 times more than Coenzyme Q10 and 500 times more than vitamin E.1Yasuhiro Nishida, E. Yamashita, Wataru Miki. Quenching activities of common hydrophilic and lipophilic antioxidants against singlet oxygen using chemiluminescence detection system. January 2007
Astaxanthin benefits
Astaxanthin has positive effects on eye health
Like lutein or zeaxanthin, astaxanthin also provides multiple benefits in vision and in the eyes health. It is known that astaxanthin accumulates in the eyes tissue and although this field needs to be more studied, studies point to its ability to improve some areas of vision.
These three antioxidants work in a way that by decreasing free radicals such as superoxides and hydrogen peroxides, they decrease the damage to the retina caused by UVA rays exposure and they increase the DNA’s repair capacity.2Santocono M, Zurria M, Berrettini M, Fedeli D, Falcioni G. Influence of astaxanthin, zeaxanthin and lutein on DNA damage and repair in UVA-irradiated cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2006;85(3):205–215. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2006.07.009
Due to its ability to reduce free radicals (in this case reactive oxygen species), astaxanthin together with other antioxidants improved the production and quality of tears in those who suffer from dry eye syndrome in a 70% of a study participants.3Huang JY, Yeh PT, Hou YC. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral antioxidant supplement therapy in patients with dry eye syndrome. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016;10:813–820. Published 2016 May 9. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S106455
In turn, today due to the high use of devices with screens, it is more common than ever to suffer from tired eyesight or computer visual syndrome, and in this case astaxanthin has been shown to increase blood flow in the eyes and to improve eye accommodation , that is, the speed with which you focus on nearby objects.4Kajita M, Tsukahara H, Kato M. The effects of a dietary supplement containing astaxanthin on the accommodation function of the eye in middle-aged and older people. Med Consult New Remedies 2009;46:89-93.
Furthermore, another study done in rats with high intraocular pressure concluded that consuming 5 mg/kg of astaxanthin for 8 weeks exerted a protective effect against ocular hypertension.5Cort A, Ozturk N, Akpinar D, et al. Suppressive effect of astaxanthin on retinal injury induced by elevated intraocular pressure. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;58(1):121–130. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2010.05.001
Astaxanthin improves skin condition and increases its UV protection capacity
A study indicates that astaxanthin prevents some of the UV rays damage by taking 4 mg for 9 weeks.6Ito N, Seki S, Ueda F. The Protective Role of Astaxanthin for UV-Induced Skin Deterioration in Healthy People-A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2018;10(7):817. Published 2018 Jun 25. doi:10.3390/nu10070817
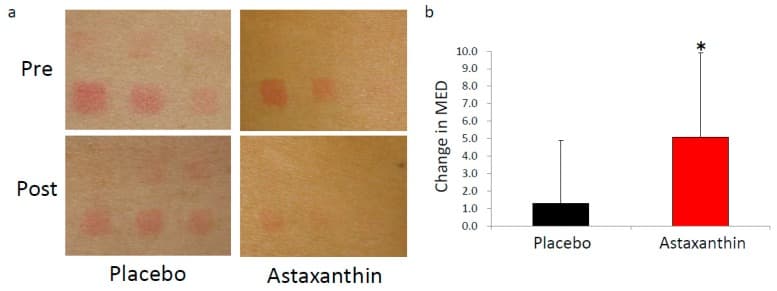
Compared to placebo, astaxanthin was able to increase the MED (minimum amount of UV rays to produce a sunburn) after taking it for 9 weeks.
In addition to lowering burns intensity, it also lowers the hydration level that the skin loses after sun exposure (up to 60% less) and increases the ability to repair DNA damaged by solar radiation.
Furthermore, various studies have shown that astaxanthin improves many skin parameters7Davinelli S, Nielsen ME, Scapagnini G. Astaxanthin in Skin Health, Repair, and Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2018;10(4):522. Published 2018 Apr 22. doi:10.3390/nu10040522 including: the hydration levels, elasticity and wrinkles.
Its main mechanisms of action are the inhibition of collagenase (an enzyme that damages collagen), free radicals and inflammation meters. A perfect combo to combat that makes it one of the best supplements to fight against skin aging.
Furthermore, since astaxanthin accumulates in the skin as it happens with the rest of carotenoids, the skin color will become more pleasant and somewhat pinker if it is consumed in large doses for a long period of time.
It improves brain function and prevents its deterioration
Astaxanthin plays a role as a neuroprotector due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier where it exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties and prevents apoptosis (cell death).8Galasso C, Orefice I, Pellone P, et al. On the Neuroprotective Role of Astaxanthin: New Perspectives?. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(8):247. Published 2018 Jul 24. doi:10.3390/md16080247
Due to these properties, astaxanthin plays a role in reducing mental deterioration in the elderly, and may delay the development of the effects of Alzheimer disease and dementia.
Furthermore, astaxanthin has also shown to improve cognitive function, as a study evaluated the efficacy of 12 mg or 6 mg of astaxanthin daily for 12 weeks in healthy individuals, showing better results in the 12 mg group.9Katagiri M, Satoh A, Tsuji S, Shirasawa T. Effects of astaxanthin-rich Haematococcus pluvialis extract on cognitive function: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012;51(2):102–107. doi:10.3164/jcbn.D-11-00017
It improves male fertility
A study funded by Astareal (A brand of astaxanthin) where infertile men received 16 mg of astaxanthin or placebo for three months concluded that astaxanthin has a positive effect on sperm quality and fertility.10Comhaire FH, El Garem Y, Mahmoud A, Eertmans F, Schoonjans F. Combined conventional/antioxidant “Astaxanthin” treatment for male infertility: a double blind, randomized trial. Asian J Androl. 2005;7(3):257–262. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7262.2005.00047.x
This can be explained by the fact that taking large amounts of antioxidants increases semen quality and motility.11Eskenazi B, Kidd SA, Marks AR, Sloter E, Block G, Wyrobek AJ. Antioxidant intake is associated with semen quality in healthy men. Hum Reprod. 2005;20(4):1006–1012. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh725
Although there is too much to be investigated yet to fully verify its effectiveness on fertility, the results of the study were promising since the total number of pregnancies that occurred in the placebo group were 10.5%, while those who received astaxanthin were 54.5%.
It decreases muscle damage
In relation to physical performance, some studies in humans have shown that astaxanthin does not present any improvement compared to placebo, but it has shown to decrease muscle damage, due to the fact that exercise produces oxidative stress and part of the free radicals produced are neutralized by astaxanthin.12Djordjevic B, Baralic I, Kotur-Stevuljevic J, et al. Effect of astaxanthin supplementation on muscle damage and oxidative stress markers in elite young soccer players. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2012;52(4):382–392.
Astaxanthin dose
In the studies mentioned above, astaxanthin is generally consumed in a range of 4 mg to 16 mg daily. Depending on the benefits you want to achieve:
- For the skin: 4 mg are enough to exert a protective effect against UV rays, for hydration and wrinkles, 6mg to 12mg have been used.
- For the eyesight: It depends on what you want to achieve, from 4 mg to 12 mg will be enough.
- For cognitive health: 6 to 12 mg, being 12 mg more effective.
- For fertility: 16 mg were used in the cited study.
- To prevent muscle damage: 4 mg has proven to be sufficient.
Astaxanthin should always be consumed right after food or together with food, since it is fat soluble and it is better absorbed with fats, so consuming it without fats would reduce its absorption considerably.
We are not responsible for the effects that the consumption of astaxanthin may cause, these are just orientation doses and you should consult a health specialist or follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Astaxanthin toxicity and side effects
Astaxanthin from H. pluvialis algae is approved in most countries as a dietary supplement and has not shown to have any side effects up to doses of 4 mg per day according to one study, although in other studies with higher doses participants reported no side effects.5Davinelli S, Nielsen ME, Scapagnini G. Astaxanthin in Skin Health, Repair, and Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients. 2018;10(4):522. Published 2018 Apr 22. doi:10.3390/nu10040522
Besides, it has been safely used in higher doses, at least over a 12-week time period in which one study used 40 mg daily.
The European Food Safety Authority concluded that it is safe to take up to 8 mg of astaxanthin daily in adults.
Although as mentioned above, no side effects have been reported in its consumption, it may cause:
- Diarrhea, upset stomach, or change in bowel movements.
- Changes to a deep pink skin tone if it is consumed in large quantities, although when you stop consuming it, the skin color returns to its original state.

